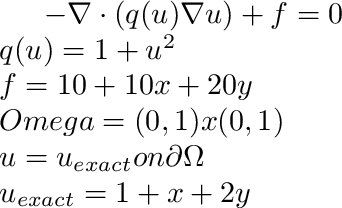|
AdH Kraken 0.0.0
Next generation Adaptive Hydraulics
|
 |
AdH Kraken 0.0.0
Next generation Adaptive Hydraulics
|
#include "adh.h"Functions | |
| int | poisson_residual (SMODEL_SUPER *mod, double *elem_rhs, int ie, double perturbation, int perturb_node, int perturb_var, int perturb_sign, int DEBUG) |
| Returns the 2D Poisson residual (linear or nonlinear), used for testing. More... | |
This file collections functions responsible for the 2D Poisson equation with constant RHS, used for testing and 2D nonlinear Poisson equation for testing
| int poisson_residual | ( | SMODEL_SUPER * | mod, |
| double * | elem_rhs, | ||
| int | ie, | ||
| double | perturbation, | ||
| int | perturb_node, | ||
| int | perturb_var, | ||
| int | perturb_sign, | ||
| int | DEBUG | ||
| ) |
Returns the 2D Poisson residual (linear or nonlinear), used for testing.
| [in] | mod | (SMODEL_SUPER*) - pointer to SMODEL_SUPER struct |
| [in,out] | elem_rhs | (double*) - array of doubles that will store elemental residual |
| [in] | ie | (int) - the elemental id |
| [in] | pertubation | (double) - the Newton pertubation |
| [in] | perturb_node | (int) - the node to be pertubed |
| [in] | perturb_var | (int) - the variable code to be perturbed |
| [in] | perturb_sign | (int) - the direction of Newton perturbation (-1 or +1) |
| [in] | DEBUG | (int) - a debug flag |
If mod->LINEAR then solves the body integals of the following weak, discrete body terms of the 2D Poisson equation:
![]() If it is nonlinear then solves:
If it is nonlinear then solves: